Encl. (1) to COMDTINST 3500.2
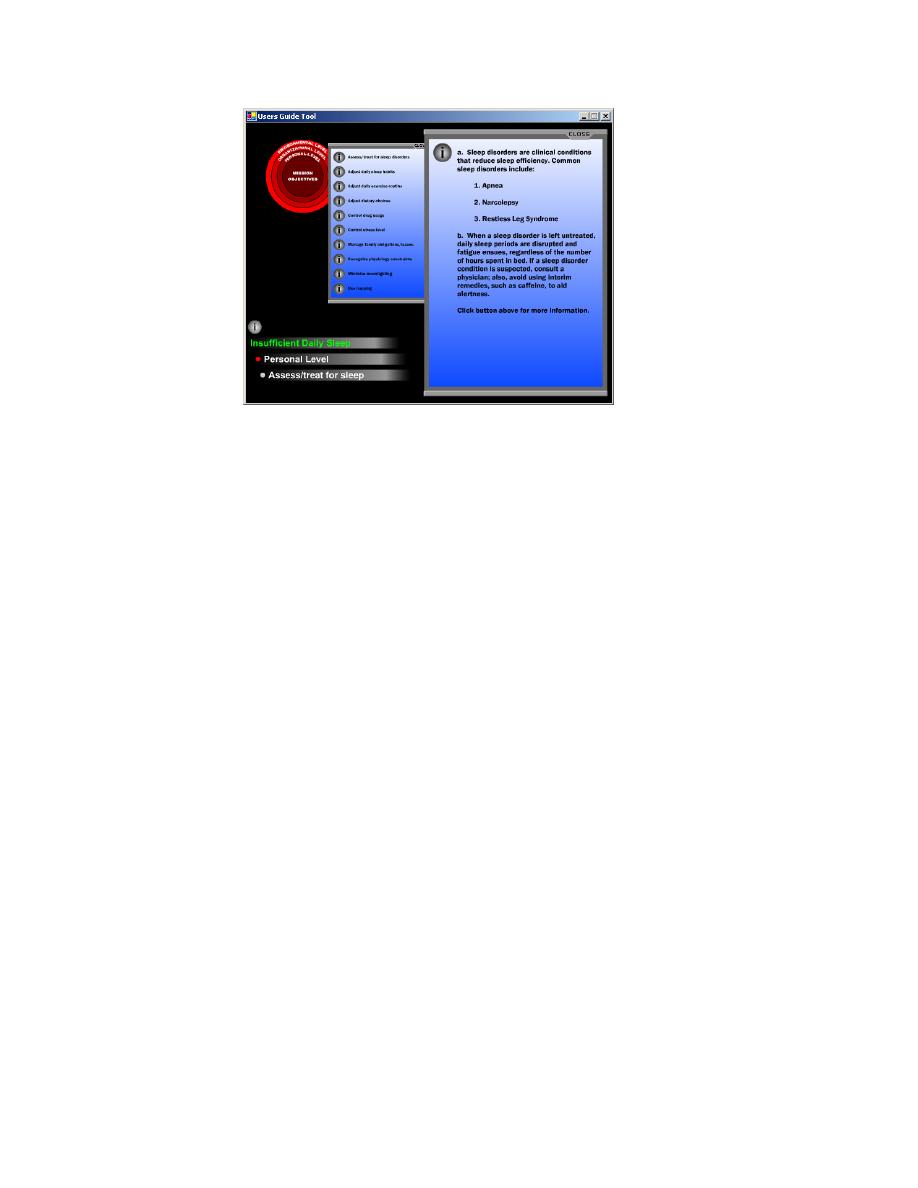
Figure 6. Specific control (Assess/treat sleep disorder) for the Personal Level.
It is recommended that the WG record each potential control and answer the following
questions concerning it: (1) What risk factor does it control; (2) Why will it control this
risk factor; (3) How will it control this risk factor? The answer to these questions will
help the WG determine if and how the control might affect other levels of the system.
It is also helpful to categorize potential controls into three groups: immediate, mid-range,
and long-term.
Immediate controls can be implemented on the spot and do not require much
effort or resources. Examples include installing door-assists to prevent slamming
in berthing areas, hanging signs that mandate `quiet areas', and reducing or
eliminating pipes during specific times of day.
Mid-range controls require some time to plan and/or resources to implement.
Examples include installing new mattresses, curtains, and air
conditioning/filtration systems in sleep environments.
Long-term controls often require substantial resources or the kind of
infrastructure changes that can only be accomplished during yard or refurbishing
periods. Examples of controls include improving ventilation systems or berthing
areas, and adding exercise and recreational facilities.
Example - Endurance management plan development
An actual endurance management plan is presented below to illustrate the thoughts,
activities, and documentation of one WG executing Step 3 of the CEM implementation
process.
7




 Previous Page
Previous Page
